| |
Key Coverage
- Explaining the concept of budget and its key components
- Stages of the budget cycle and key relevant issues at each stage that are practiced in Bangladesh.
- Navigating through the Budget and budget calendar.
- Key actors along the budget cycle with their roles and responsibilities.
- Parliamentary Oversight
Budget Defined
- A budget (from old French bougette, purse) is a financial plan and a list of all planned expenses and revenues.
- A government budget is a legal document that is often passed by the legislature, and approved by the chief executive-or president.
- The two basic elements :Revenues and Expenses.
- Revenues are derived primarily from taxes and non-tax revenue.
- Government expenses include spending on current goods and services, which economists call government consumption ; government investment expenditures such as infrastructure investment or research expenditure; and transfer payments like unemployment or retirement benefits, Social Safety nets
Basis of Budget
- Budgets have an economic, political and technical basis.
- Unlike a pure economic budget, they are not entirely designed to allocate scarce resources for the best economic use.
- They also have a political basis wherein different interests push and pull in an attempt to obtain benefits and avoid burdens.
- The technical element is the forecast of the likely levels of revenues and expenses
Budget Cycle
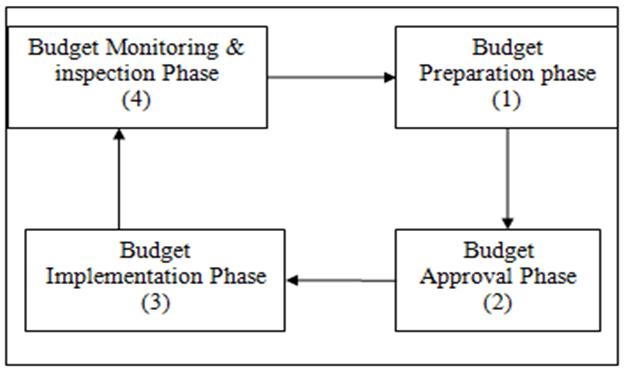
- Budget Preparation: The first phase of the budget cycle involves preparation by the departments/agencies, ministries and finally ministry of Finance
- Legislative Approval: Typically, the legislature has the power to approve or reject a proposed budget. They review it and vote. If approved, it moves into the implementation phase.
- Implementation and Execution: It is the duty of the executive branch - primarily involves distributing the budgeted resources to their designated recipients within the government and spending it as planned.
- Audit and Review: Finally, a budget is typically audited and reviewed following implementation to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness in order to guide future budgeting decisions.
Types Of Budget (By Income-Expenditure Relationship)
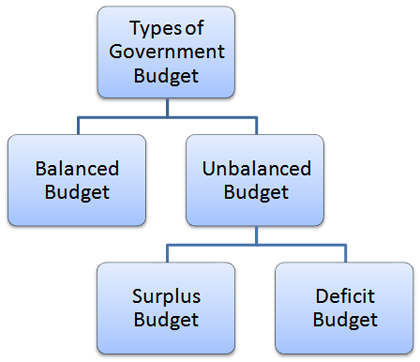
Different Types of Budget
- Traditional incremental budgeting justify only variances versus past years actual expenditure, based on the assumption that the "baseline" is automatically approved
- Zero based budgeting every line item of the budget must be approved, rather than only changes. During the review process, no reference is made to the previous level of expenditure (Reverse to Traditional).
- Performance based budgeting is the practice of developing budgets based on the relationship between program funding levels and expected results from that program.
- Medium Term Budget Framework is a budgeting approach that links Government’s policy priorities to resource allocations and resource allocations to performance. Emphasizes the efficient use of limited public resources (both development and non-development) And accounts for the results
- Program budgeting developed by U.S. president Lyndon Johnson, describes and gives the detailed costs of every activity or programme that is to be carried out in a budget. Objectives, outputs and expected results are described fully as are their necessary resource costs, for example, raw materials, equipment and staff. The sum of all activities or programmes constitute the Programme Budget.
Budget in Bangladesh: Legal Framework
- Constitution of Bangladesh, 1972 (Ch.II, Legislative and Financial Procedure, Article 80-92, 87-Annual Financial statement)
- Rules of Procedure of Parliament of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh 1973 (Rule-111-127)
- General Financial Rules, 1951, updated 1998 (Budget, Grants and Appropriations)
- Preparation of the Budget (Secretariat Instruction, 1976 updated 2008)
- The Public Moneys & Budget Management Act, 2009
Institutional Framework
Ministry of Finance mainly responsible to prepare and place the budget before the parliament. 3 divisions involved:
1. Finance Division
2. Economic Relations Division
3. Internal Resources Division (National Board of Revenue)
Other Ministries/Agencies:
- Planning Commission
- Line Ministry/Division/ Agencies
Budgeting Concepts
Revenue = Tax + Non-tax
Expenditure = Revenue +Development
Expenditure – receipts = Deficit
Deficit Financing requires Borrowing
-From External Sources
Loans, Grants, project Aid
-From Domestic Sources
Loans From Banks
Loans From Non Banking sources
Budget Calendar
SI. |
Particulars |
Due date |
1 |
Printing of departmental estimates |
31 July |
2 |
Printing and distribution of budget (estimating officer's forms and controlling officer's forms) |
31 August |
3 |
Preparation, printing and supply of budget form to the Accounts officer concerned |
30 September |
4 |
Submission of estimates by estimating officers |
10 October |
5 |
Receipt of estimates in the Accounts office and the Ministry of Finance from controlling officers with three months accruals |
31 October |
6 |
Receipt of consolidated estimates in the ministry of Finance with three month's accruals from the Accounts Officer |
25 November |
7 |
Completion of examination of budget estimates in the MoF Finance |
20 January |
8 |
Receipt of schedule of new expenditure in the MoF |
22 January |
9 |
Receipt of six month's accruals from the NO |
15 February |
10 |
Completion of review of estimates on the basis of six month's accruals in the fv1oF |
28 February |
11 |
Preparation and dispatch of first edition of the budget and the schedule of new expenditure |
1 March |
12 |
Receipt back of the first edition of budget from press and dispatch to ministries/ divisions |
10 march |
13 |
Forecast of foreign assistance for development program |
14 march |
14 |
Completion of discussion on estimates with administrative ministries/divisions |
28 march |
15 |
Receipt of final annual development program from the ministry of planning |
28 march |
16 |
Preparation and printing of budget documents |
May |
Budget Making Process
- Bangladesh started implementing MTBF in 2004-05 and completed over 5 years.
- At the helm is the BMRC (Budget Monitoring and Resource Committee)
- Headed by the Minister for Finance and performs the functions of co-ordination of the overall resources and expenditure programmes of the government;
- Finalises the estimates of domestic resources. After determination of requirements for the non-development budget, the remaining internal resources are set aside for the development budget.
MTBF: Different Stages of preparation
- Firstly, Finance Division issue BC-1 with Preliminary Indicative Expenditure Ceiling for each Line Ministry
- Secondly, Line Ministry prepare Ministry Budget Framework (MBF) with the help of departments/agencies (up to district level)
- Thirdly, Finance Division and Planning Commission jointly review and finalize agreed Budget numbers and MBFs
- Fourthly, Finance Division issue Budget Circular-2 with Ministry-wise Indicative Expenditure Ceilings
- Fifthly the estimates are reviewed and finalized by FD
- Finally, Budget is presented to the Parliament
Core Budget Documents Placed before the parliament
- Budget Speech of the Finance Minister
- Budget in Brief
- Annual Financial Statement
- Supplementary Budget (Additional demand for grants for the ongoing year)
- Combined Demand for Grants
- Consolidated Fund Receipt
- Medium Term Budget Framework
- Detailed Budget
- Annual Development Program(ADP)
- Gender Budget
- Bangladesh Economic Review
Ministry Budget Framework (MBF): Overview
- Ministry Budget Framework (MBF) is divided into two major Parts and five Sections
- Part-A is prepared by the Ministry or Division
- Part-B to be prepared by Departments/ Agencies under the respective Ministry/Division
Part-A of the MBF : Section 1
1.1 Mission Statement of the Ministry/Division
- To develop a clear mission statement, the ministry must consider the following:
- What is the purpose of this ministry; what does it intend to achieve,
- By what broad areas of operation will the ministry do this, and
- Who are the intended beneficiaries?
- Mission Statement should be brief – If it cannot be remembered by staff, it is not useful
1.2 Major Functions of the Ministry/Division
- List the major functions of the ministry/ division
- These should be summarised from the Allocation of Business
- These should, in general, be limited to a maximum of 8 functions
Part-A of the MBF: Section 2
Medium-Term Strategic Objectives and Key Activities
Strategic Objectives |
Key Activities |
Departments or Agencies |
1 |
2 |
3 |
Set out the key strategic objectives for the ministry/division as a whole.
These should be derived and summarised from the NSAPR and/or ministry/sector policy documents.
Keep the list of strategic objectives short by combining some closely related objectives.
List only objectives, and exclude strategies or activities (policy agenda) |
An activity is a description of what is to be done with the resources provided through the budget.
Identify the key activities of the ministry/division which are expected to contribute towards the realisation of the strategic objective. These activities should be consistent with the functions of the ministry/division.
Limit the number of activities to a maximum of 6 per strategic objective. |
List the directorates/agencies that will be responsible for the implementing the key activities.
Only include departments/ agencies that have a direct and significant role in undertaking the activities listed against each objective. |
Part-A of the MBF: Section 3
- 3.1 Impact of Strategic Objectives on Poverty Reduction and Women's Advancement
- The strategic objectives to be listed in this section are same as in section 2
- Describe how the strategic objectives and their associated activities relate and contribute to the Government’s wider objectives of poverty reduction and women’s advancement.
- 3.2 PR&WA Related Spending
Part-A of the MBF: Section 4:
Priority Spending Areas/Programmes
Priority Spending Area/Programmes |
Related Strategic Objectives |
Priority spending area is a ‘defined programme of activities or works that makes a significant contribution towards the realisation of the strategic objectives of an organisation.
Identify and describe the main priority spending areas for the ministry/division that are expected to have the greatest impact on the achievement of ministry/division’s strategic objectives.
These should relate to the main functions of the ministry/division and should be ranked in order of priority.
Limit the number of priority spending areas to a maximum of 6.
Summarise the description within a single paragraph (40-60 words). |
For each priority spending area list the relevant strategic objective to which it is expected to contribute. |
Part-A of the MBF: Form # 1
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) - Ministry
Indicator |
Related Strategic Objectives |
Unit of Measurement |
Target |
Actual |
Target |
Revised Target |
Medium-Term Target |
2009/10 |
2009/10 |
2010/11 |
2010/11 |
2011/12 |
2012/13 |
2013/14 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
Indicator 1: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicator 2: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicator 3: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indicator 4: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
KPIsshould meet the SMART criteria:
- Specific – the indicator is clearly defined
- Measurable – Stated in verifiable or quantifiable terms
- Achievable – the indicator targets are realistically set
- Relevant – the indicator is relevant to the objective
- Time bound - there is a clear timeframe for achieving the target
Part-B of the MBF: Section 5
- 5.1.1 Recent Achievements
- A brief narrative of recent achievements. The description should include recent data and provide a good account of the scope and scale of the activities undertaken
Part-B of the MBF: Section 5
5.2: Key Activities, Outputs related to the Activity
- From the activities that were identified by the in Part A Section 2, list those that are carried out by the department/agency
- Describe the total outputs to be achieved within the total life of the activity
5.3 Output Indicators and Targets
- 3 indicators that best summaries the key outputs of the department/agency
- A further 2 indicators may be included for outputs related to the objectives of poverty
Part-B of the MBF: Section 5
5.4 Forward Budget Estimates
MBF document will include a table showing the budget estimates for the next FY and forecast for the subsequent two years for the department
5.5 List of Projects and Programmes
- Name of the approved projects/programmes
- Name of the un-approved projects/programmes
- Name of the Probable Projects/Programmes
IMPLEMENTATION ARRANGEMENTS
Three key organizational units responsible for the MTBF implementation in ascending order of hierarchy:
- Budget wing/branch/section to prepare drafts of MBF with budget allocations
- Budget Working Group (BWG) to support the Budget Management Committee (BMC) for decision making on MBF
- Consists of representatives of organizational units of the Ministry and of Finance Division and Planning Commission
- BMC - the budget approval authority within the line ministry
- Led by the Secretary, and
- Consists of Additional and Joint Secretaries, Organizational Heads, and representatives of FD, PC, IMED & CAO
Financial Oversight
Parliament is the custodian of public fund according the constitution
Budget discussed and approved in the Parliament
Cannot be placed before a committee
Parliament performs oversight functions on the execution and implementation through
- Public Accounts Committee
- Public Undertakings Committee
- Estimates committee
- Committee on ministry of finance
- Standing Committees on different Ministries
Conclusion
- Budget is a complex issue dealt by the Finance people and always kept away from general mass
- Bangladesh has undergone Series of reforms in PFM
- Discarded old incremental budget making process having no connection to plan and performance
- Introduced MTBF or MTEF system connecting policy priorities to resource allocations and resource allocations to performance
- Ministries/Divisions have more control over resource allocation and determining priorities
- Defining key performance indicators prior to budget helps to measure performance of the budget and redefine priorities
- It is not the whole picture; we tried to get an overview
|